General information
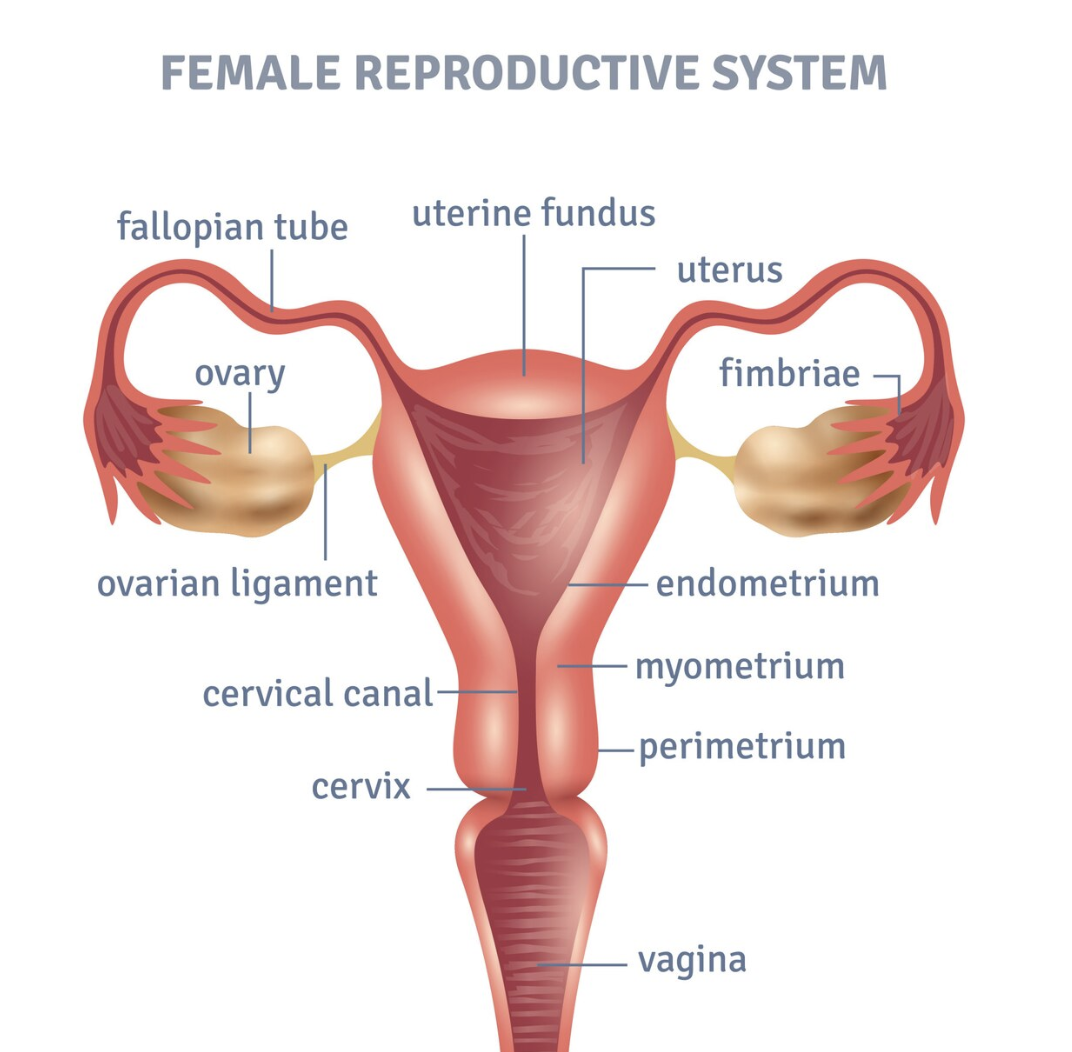
As known, women ovulate once a month; at this time, an egg is released from the ovary and enters the fallopian tube, where it stays for 24-36 hours. Following intercourse, the ovulated egg in the fallopian tube will meet spermatozoa, one of which will “unite” with the egg and fertilize it. The now fertilized egg will leave the fallopian tube within 2-3 days to travel into the uterus, where it is implanted in the uterine lining and grows into an embryo.
If pregnancy is not achieved, the uterine lining (endometrium) is shed as monthly menses and a new ovulation cycle begins.
Ultrasound screening of ovarian follicular development and determination of the day of ovulation may help couples trying to conceive. The screening is performed by a transvaginal ultrasound and no longer requires a full bladder.
If ovulation is not regular, drugs can be given at the beginning of the cycle to stimulate it, which may also induce the development of multiple ovarian follicles. The follicle is a small fluid-filled pouch in which the egg grows and matures.
The production of multiple eggs increases the chance of conception per cycle, and it also increases the odds of a multiple pregnancy (twins, triplets, etc.).
In such cases, the type of treatment, dosage and combination of drugs are tailored to cover the needs of each couple. The doctors in the special assisted reproduction unit at "GENESIS ATHENS" will discuss your problem in detail and the recommended treatment, and will answer all your questions.
Source: https://www.genesisathens.gr/en/
© 2025 IVF counseling and assistance service | All Rights Reserved
